OPERA catches its first tau neutrino
Updated: 2010-05-31 12:49:34
 Scientists from the OPERA experiment at INFN's Gran Sasso National Laboratory have announced the first direct observation of a neutrino transforming from one type into another. When confirmed by a few more such events, this observation will provide further strong evidence that neutrinos have mass, a phenomenon that remains unexplained by physicists' recipe for understanding the universe, the Standard Model.
Scientists from the OPERA experiment at INFN's Gran Sasso National Laboratory have announced the first direct observation of a neutrino transforming from one type into another. When confirmed by a few more such events, this observation will provide further strong evidence that neutrinos have mass, a phenomenon that remains unexplained by physicists' recipe for understanding the universe, the Standard Model. 
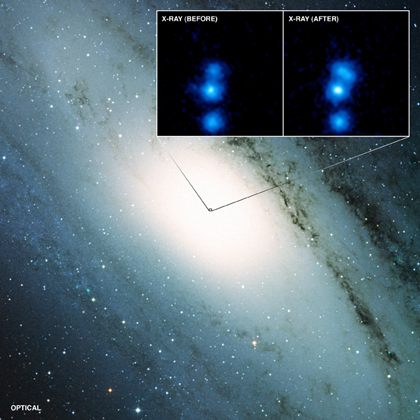 The large image here shows an optical view, with the Digitized Sky Survey, of the Andromeda Galaxy, otherwise known as M31.
The large image here shows an optical view, with the Digitized Sky Survey, of the Andromeda Galaxy, otherwise known as M31. Studies of Hubble Space Telescope images of the distant Universe revealed that the galaxy types seen nearby were still present, but generally become "messier" the further back in time one looks. Furthermore, there appeared to be types of distant galaxies that we do not see today. Many of these galaxies comprise knots or clumps, forming "chains", "tadpoles" and "clump clusters".
Studies of Hubble Space Telescope images of the distant Universe revealed that the galaxy types seen nearby were still present, but generally become "messier" the further back in time one looks. Furthermore, there appeared to be types of distant galaxies that we do not see today. Many of these galaxies comprise knots or clumps, forming "chains", "tadpoles" and "clump clusters". Scientists of the DZero collaboration at the Department of Energy's Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory announced Friday, May 14, that they have found evidence for significant violation of matter-antimatter symmetry in the behavior of particles containing bottom quarks beyond what is expected in the current theory, the Standard Model of particle physics.
Scientists of the DZero collaboration at the Department of Energy's Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory announced Friday, May 14, that they have found evidence for significant violation of matter-antimatter symmetry in the behavior of particles containing bottom quarks beyond what is expected in the current theory, the Standard Model of particle physics. Can you tell a gravitational lens from a spiral galaxy? With an expansion of the Galaxy Zoo citizen science project, you can try your eye at lens identification, thanks in part to the efforts of Phil Marshall at SLAC and Stanford's Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophyics and Cosmology.
Can you tell a gravitational lens from a spiral galaxy? With an expansion of the Galaxy Zoo citizen science project, you can try your eye at lens identification, thanks in part to the efforts of Phil Marshall at SLAC and Stanford's Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophyics and Cosmology. At a distance of about 400 million light years from Earth, a massive "wall" of galaxies stretching tens of millions of light years.
At a distance of about 400 million light years from Earth, a massive "wall" of galaxies stretching tens of millions of light years.